| Home |
| Where to Start |
| News and Updates |
| Tutorials |
| Data Products |
| Data Access |
| Sky Coverage |
| Instruments |
| Data Flow |
| Algorithms |
| Glossary |
| Known Problems |
| Help and Feedback |
| Search |
 |
Glossary of SDSS TerminologyThis page contains a comprehensive glossary of SDSS-related terminology. Terms are given in alphabetical order, with definitions and links to extended descriptions where available. If you come across a term you don't understand, or think we should include, please write to sdss-helpdesk@fnal.gov. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y ZAadaptive momentsA method of measuring object shapes. These moments are close to optimal for measuring the shapes of faint galaxies, and have been used for weak lensing studies. See the Adaptive Moments section of the algorithms pages.APOApache Point Observatory, located in Sunspot, New Mexico. This is the location of the 2.5m SDSS telescope as well as the Photometric Telescope (PT), as well as other non-SDSS telescopes. See APO homepage.ARCAstrophysical Research Consortium. Body that owns and operates APO.asinh magnitudeMagnitudes within the SDSS are expressed as inverse hyperbolic sine (or ``asinh'') magnitudes, sometimes referred to informally as luptitudes . The transformation from linear flux measurements to asinh magnitudes is designed to be virtually identical to the standard astronomical magnitude at high signal-to-noise ratio, but to switch over to linear behavior at low S/N and even at negative values of flux, where the logarithm in the Pogson magnitude fails. Details can be found in the Photometry section of the Algorithms pages, or the actual Lupton et al. 1999 AJ paper.asTrans fileFITS binary table with astrometric transformations for every field in a single imaging run. It transforms frame (row,col) coordinates to great circle (mu,nu) coordinates for a given inclination. Available in the DAS.AstroDAThe data acquisition and analysis system used to collect data from the survey telescope cameras.AstromThe data processing pipeline that maps CCD pixel coordinates to celestial coordinates. The detailed workings of this pipeline are described in the Astrometry section of the algorithms pages, or the Pier et al. 2003 AJ paper.astrometric chipThe SDSS camera contains 24 2048x400 pixel CCDs (in addition to the 30 2048x2048 photometric CCDs) which are used for astrometry and focus monitoring. Because they are smaller chips, the effective exposure time is only 11 seconds, allowing the survey to observe brighter stars without saturation. These bright star positions are necessary to match to objects present in astrometric catalogs used by the Astrom pipeline. For more details on these chips, please see the appropriate section of the camera pages or the AJ imaging camera paper (Gunn et al. 1998).astrometryThe detailed methodology utilized by the SDSS is described in the Astrometry section of the algorithms pages.AstrotoolsThe collaboration's software package to run data processing. atlas imageFor each detected object, the atlas image comprises the pixels that were detected as part of the object in any filter. These are available through the DAS, as a single file for each field.BBestWe maintain multiple versions of the SDSS imaging data set. The Best version contains the images and photometric catalogs with the highest quality data at the time of the data release. The target version contains those data at the time the target selection algorithm was run for that part of the sky. The DR1 "best" data set contains better data for some parts of the sky than the DR1 "target" data set (including most of the EDR data set).binned frameEach file is a FITS image for one filter, 512 x 372 pixels, with WCS information. These are the corrected frames with detected objects removed and binned 4 pixels by 4 pixels. All pixels that are in atlas images are replaced by the background level before binning, with suitable noise added. All of the header parameters from the original image are inherited as well. Available in the DAS.Black BookSimilar to the Project Book, this document provides a description of the original science goals of the survey, as well as the hardware and software designs, and was the 1996 proposal to NASA. Please keep in mind that it is not updated, so information within it may no longer be current. Nevertheless, it provides an excellent overview of the survey. The Black Book is available online.boresightThe telescope control computer keeps track of a specific point in the telescope focal plane that is called the boresight. The boresight is not fixed in the array but is at one of two places for the two strips that compose a stripe. It is the boresight that will track great circles. Technically, the boresight tracks a path that is a great circle in J2000 coordinates as viewed from the solar system barycenter.CcalibrationThe process by which the photometric and spectroscopic observations are calibrated. The goal of calibration is to take the digital camera readouts and convert them to measured quantities, like fluxes. The details of these procedures can be found on the algorithms pages.camcolA Camcol is the output of one camera column as part of a Run. Therefore, 1 Camcol = 1/6 of a Run. It is also a portion of a scanline.cameraThe instrument used for imaging. It consists of 30 photometric and 24 astrometric CCDs (see camera description). The camera is a mosaic of 54 CCD detectors in the focal plane, 30 large devices arranged in 6 columns of 5 each and 24 smaller devices around the periphery. See this sketch of the camera focal plane or this real life image. The camera is described in detail in the imaging camera paper (Gunn et al. 1998).CAS (Catalog Archive Server)The Catalog Archive Server contains the measured parameters from all objects in the imaging survey and the spectroscopic survey. It will become available as part of the next data release.central meridianThe meridian which passes through the center of the survey area, 12h 20m , defines the central meridian of a scan. The great circle perpendicular to it passing through the survey center at =32.8deg is the survey equator. =32.8deg is the survey equator.
childA product of the deblending process. When two objects are near each other on the sky, their images may appear merged. The deblender tries to split this merged image; the resulting sub-images are called children. The initial merged image is called a parent. For more details, see the Deblending section of the algorithms pages.chunkA chunk is composed of a set of touching but non-overlapping primary segments (or parts of segments) which fills a "chunk" of a stave, and is therefore bounded on the east and west by lines of constant mu, and north-south by lines of constant eta (if in the North). Southern chunks have no eta boundary applied. A chunk may also have a lambda cut if it is at the end of the survey region for that stripe. Chunks do not overlap, so the union of all existing chunks represents the unique sky coverage for the survey at any given time. See this figure explaining the SDSS survey geometry for details. Note that the bounds on chunks, if using mu/eta, are a mix of survey coordinates and great circle coordinates. Note: The term chunk has sometimes been used to describe an area of sky that has had tiling run on it. This is properly called a tiled region.classificationThe method by which we assign a type (star or galaxy) to each object. The details of this procedure are described in the Classification section of the algorithms pages.Cloud CameraA camera at the mountain that takes continuous pictures of the sky at 10 microns, a wavelength at which clouds emit. It is a sensitive measure of the photometricity of the sky as a function of time.CMMCoordinate Measuring Machine, a device used to measure the positions of holes in the fiber mount plates for the spectrographic survey.Cmodel magnitudeComposite model magnitude. See magnitude, cmodel.coordinatesThe SDSS uses three different coordinate systems. Of course, we use standard astronomical right ascension (RA) and declination (Dec), J2000. There is also the survey coordinate system, with coordinates lambda (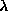 ) and eta ( ) and eta (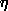 ). This is just a rotation of the usual RA, Dec
system. Finally, there is the great
circle coordinate system, which is actually a separate
coordinate system for each stripe. The
coordinates of this system are mu ( ). This is just a rotation of the usual RA, Dec
system. Finally, there is the great
circle coordinate system, which is actually a separate
coordinate system for each stripe. The
coordinates of this system are mu (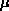 ) and nu ( ) and nu ( ). ).
corrected frameEach corrected frame is a FITS image for one filter, 2048 columns by 1489 rows, with row number increasing in the scan direction. These are the imaging frames with flat-field, bias, cosmic-ray, and pixel-defect corrections applied. A raw image contains 1361 rows, and a corrected frame has the first 128 rows of the following corrected frame appended to it. The pixels subtend 0".396 square on the sky. Header information using the world coordinate system (WCS) allows standard astronomical FITS tools to convert pixel position to right ascension and declination. Available in the DAS.CVSThe Concurrent Versions System, used by SDSS software and website developers to maintain versioning control. An open source project available at https://www.cvshome.org/.cx/cy/czThe coordinates on the unit sphere utilized by the HTM code; these are stored in the database.DDASThe Data Archive Server, which provides access to the imaging and spectroscopic products of the survey. The DAS is located at http://das.sdss.org/DR1-cgi-bin/DAS. We also provide descriptions of the DAS data access tools.data modelThe description of the structure and organization of the data in a database. The data model tells you all the tables names, their contents, and how they are related to, and linked with, one another. The actual implementation of a data model is called the database schema. For the flat files available in the DAS, the data models are available here.deblendDeblending is the process by which overlapping objects in images are separated. The frames pipeline attempts to determine whether each object actually consists of more than one object projected on the sky and, if so, to deblend such a parent object into its constituent children, self-consistently across the bands (thus, all children have measurements in all bands). For details on how this works, and what flags this procedure may set, see the Deblending section of the algorithms pages.DervishAn FNAL software toolkit used by many of the data acquisition and reduction systems.deVaucouleursAlso know as the r1/4 law, it describes the radial light profile of a typical elliptical galaxy. Defined asI(r) = I0exp{-7.67[(r/re)1/4]}. An elliptical version of this profile is fit to every detected object, yielding the deV parameters. See the model magnitude section of the photometry algorithm page for details.
DR1Data Release 1. The first major release of SDSS data to the public, occurring in March, 2003. A small portion of the data was released earlier as part of the Early Data Release (EDR).EEDREarly Data Release. The first public release of SDSS data occurred in June of 2001. This current release (DR1) includes the area present in the EDR, and more. The data has also been reprocessed with improved software. The EDR is described in the EDR paper on the AJ web site, also available as EDR paper in HTML.ellipticityMeasures how elliptical an object is. In the SDSS, we have numerous methods to measure this:
etaLatitude in the survey coordinate system. Eta is the angle between the survey equator and the great circle passing through the point perpendicular to the survey meridian, positive to the north. Constant latitude curves are great circlesexponential modelThe radial light distribution of a disk galaxy can often be fit by an exponential profile:I(r) = I0exp(-1.68r/re) The number 1.68 is chosen so that the model radius is a half-light radius. An elliptical version of this profile is fit to every detected object, yielding the exp parameters. See the model magnitude section of the photometry algorithm page for details.
FFalse color pipelineA pipeline to produce 3-color JPG files of zoomed-down SDSS images.fiberThe SDSS spectrograph uses optical fibers to direct the light from individual objects to the slithead. Each object is assigned a corresponding fiberID. The fibers are 3 arcsec in diameter in the source plane. Each fiber is surrounded by a large sheath which prevents any pair of fibers from being placed closer than 55 arcsec on the same plate.fiberMagThe fiber magnitude. See Magnitude, fiber.fieldA field is a part of a camcol that is processed by the Photo pipeline at one time. Fields are 2048x1489 pixels; a field consists of the frames in the 5 filters for the same part of the sky. Fields overlap each other by 128 rows; primaries are decided when Chunks are resolved (using objects between rows 64 and1425 as primaries). A field at the edge of a Chunk may in fact be included in 2 (or more) Chunks. See this figure explaining SDSS field geometry for details.filterA piece of material used to allow only specific colors (or wavelengths) of light to pass through. The SDSS uses five filters: u,g,r,i,z. However, defining standards and absolute calibration for these filters has been difficult. Please read the Camera Page for details.FITSThe Flexible Image Transport System, a standard method of storing astonomical data. The FITS format has a home page.flagA bitmask used in the database to specify various properties of an object. There are many flags in the SDSS catalogs which tell the user extremely important and useful pieces of information, such as whether the object was deblended or saturated, for instance. There are status flags set by PSP, and by survey operations, on a frame-by-frame basis, describing the quality of the PSF, and the quality of the data overall. Each object is given status flags that sort out overlaps. And the spectra have flags at two levels as well: pixel-by-pixel flags, and warning flags accompanying the redshifts and classification to indicate trouble. For more help with flags, see the Flags Help Page.FNALFermi National Accelerator Laboratory, one of the participating institutions in SDSS. Their homepage is http://www.fnal.gov.footprintThe area on the sky covered by the SDSS. The footprint released for DR1 is described on the sky coverage page.fpAtlas fileA FITS binary table containing the atlas images for all objects detected in all five filters in a single field. Requires special software to decode into individual FITS images for each object. The FITS images are available in the DAS.fpBin fileSee binned frame.fpC fileSee corrected frame.fpFieldStat fileA binary FITS table containing a statistical summary of the results of the frames pipeline for one field for a single frames pipeline run. This information is also found in the Field table in the CAS database. Available in the DAS.fpM fileSee mask frame.fpObjc fileThese are FITS binary tables containing catalogs of detected objects output by the frames pipeline. These are uncalibrated, as opposed to the tsObj files, with no targeting information. Available in the DAS.frameThe data stream from a single CCD in a scanline is cut into a series of frames which measure 2048 x 1489 pixels and overlap 10% with the adjacent frame. The frames in the 5 filters for the same part of the sky are called a field.frames pipelineIn this pipeline, the images are bias-subtracted and flat-fielded, and bad columns, cosmic rays, and bleed trails are interpolated over. This yields corrected frames. Then objects are found by running a PSF-matched filter over the image, and matched up between the five frames making up a field. A deblender is run to resolve overlaps, and the properties of each object are written to the fpObjc files. Atlas images are written to the fpAtlas files.fundamental standardThe photometry of the primary standard stars is ultimately tied to the SED of the star BD 17 +4708, which is the fundamental standard for the SDSS photometric system. See the Smith et al. 2002 AJ paper for more details.GGNATSThe system used to report and track bugs and issues with SDSS hardware and software; for collaboration use only.great circle coordinatesOne of the two main coordinate systems utilized by the SDSS. In this system, mu and nu are spherical coordinates (corresponding to ra and dec) in a system whose equator is along the center of the stripe in question. The stripes of the survey are great circles which all cross at (RA, Dec) = (95, 0). The stripes are defined by their inclination with respect to the equator, and are indexed by integers n such that the inclination of a stripe is -25 + 2.5n. Thus, stripe n=10 corresponds to the Equator. The design is that the area covered by the imaging on a given stripe (the so-called OK_SCANLINE area in the north) is a 2.5 degree wide rectangle centered on nu=0 in Great Circle coordinates.HHTMThe Hierarchical Triangular Mesh (HTM) is a partitioning scheme to divide the surface of the unit sphere into spherical triangles. It is a hierarchical scheme and the subdivisions have not exactly, but roughly equal areas. HTM is used to index the coordinates in the object databases for faster querying speeds. For more details, and downloadable software, see the HTM Website.HoggPTA program which runs on the mountain, which uses information from the photometric telescope and the cloud camera to determine the photometricity of a given night. It was written by David Hogg and colleagues, thus its name.holeA field or set of fields which is missing from the data, either because of non-photometric conditions, tracking problems, very poor seeing, or simply because that area has not been surveyed yet. This is encoded in the status flags.IIOPImaging Observers Program. The software that runs the imaging camera on the survey telescope.JJHUJohns Hopkins University, one of the participating institutions in SDSS. The SDSS JHU homepage is http://www.sdss.jhu.edu.JPGJapan Participation Group, one of the participating institutions in SDSS. Their homepage is http://hikari.astron.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/work/SDSS/sdss.html.KLlambdaOne of the coordinates of the survey coordinate system. The stripe longitude lambda is measured from the survey central meridian positive to the east along the great circles perpendicular to that meridian. Constant longitude curves are circles centered on the survey poles .luptitudeAn informal name for the asinh magnitude.MmaggieA maggie is a linear measure of flux; one maggie has an AB magnitude of 0 (thus a surface brightness of 20 mag/square arcsec corresponds to 10-8 maggies per square arcsec). This unit is used for object radial profiles, where we provide the azimuthally averaged object surface brightness in a series of annuli.magnitude, cmodelComposite model magnitude. The magnitude obtained from the best-fitting linear combination of the best-fitting de Vaucouleurs and exponential model for an object's light profile (cf. magnitude, model). See cmodel magnitude description in Photometry section of the Algorithms pages.magnitude, fiberThe flux contained within the aperture of a spectroscopic fiber (3" in diameter) is calculated in each band and stored in fiberMag. Details can be found in the Photometry section of the Algorithms pages.magnitude, modelJust as the PSF magnitudes are optimal measures of the fluxes of stars, the optimal measure of the flux of a galaxy would use a matched galaxy model. With this in mind, the code fits two models to the two-dimensional image of each object in each band:1. a pure deVaucouleurs profile, and 2. a pure exponential profile. The best-fit model in the r-band is fit to the other four bands; the results are stored as the model magnitudes. Details, including a very important warning, can be found in the Photometry section of the Algorithms pages. magnitude, PetrosianStored as petroMag. For galaxy photometry, measuring flux is more difficult than for stars, because galaxies do not all have the same radial surface brightness profile, and have no sharp edges. In order to avoid biases, we wish to measure a constant fraction of the total light, independent of the position and distance of the object. To satisfy these requirements, the SDSS has adopted a modified form of the Petrosian (1976) system, measuring galaxy fluxes within a circular aperture whose radius is defined by the shape of the azimuthally averaged light profile. Details can be found in the Photometry section of the Algorithms pages and the Strauss et al. 2002 AJ paper on galaxy target selection.magnitude, PogsonThe Pogson magnitude is the standard astronomical magnitude system, where one increment in magnitude is an increase in brightness by the fifth root of 100. A star of 1st magnitude is therefore 100 times as bright as a star of 6th magnitude. That is, for two objectsM1 - M2 =
-2.5log(F1/F2)where M1 and M2 are the magnitudes of two objects, and F1 and F2 are their luminous fluxes. magnitude, PSFStored as psfMag. For isolated stars, which are well-described by the point spread function (PSF), the optimal measure of the total flux is determined by fitting a PSF model to the object. Details can be found in the Photometry section of the Algorithms pages.maskmask frameEach file is a binary FITS table for one filter. Each row of the table describes a set of pixels in the corrected frame, using mask values described in Table 8. Available in the DAS.MASTThe Multimission Archive at Space Telescope. Data from a variety of space missions and ground-based telescopes is provided, including the Sloan EDR. The site is located here.modelMagThe model magnitude. See magnitude, model.Monitor Telescope (MT)The previous incarnation of the Photometric Telescope (PT).MT fieldSee secondary patch.mtpipeThe pipeline for processing data from the Photometric Telescope. A description can be found in the appropriate section of the EDR paper.muOne of the coordinates in the SDSS great circle coordinate system. Mu corresponds to RA, or longitude.NnfCalibThe pipeline that uses the results of MTPipe and astrom to apply the photometric and astrometric calibration to each object in the imaging data.nuOne of the coordinates in the SDSS great circle coordinate system. Nu corresponds to Dec, or latitude.OobjectEnumerates photometric objects within a given field. Thus, multiple fields may have objects with the same object number.ObjectivityA brand of object-oriented database used to initially serve the EDR and to run OpDB.ObjIDThe long object identification, which is a bit-encoded integer of run, rerun, camcol, field, object. When the data is reprocessed (rerun), this number will change! IMPORTANT NOTE: For spectroscopic objects, there are two possible choices for the matching photometric measurement: TargetObjID is the photometric object identification number of the corresponding photometric object when targeting was run, and BestObjID, which points to the best imaging and processing of the photometry.OpDBThe survey's internal Operations Database at FNAL.Ppar fileAlso known as a Yanny parameter file. This is a simple ascii file format developed to store lists of parameters for the SDSS, such as the survey coverage description.parentA product of the deblending process. When two objects are near each other on the sky, their images may appear merged. The deblender tries to split this merged image; the initial merged image is called a parent, while the resulting sub-images are called children. For more details, see the Deblending section of the algorithms pages.participating institutionOne of the institutions involved in the survey. These institutions have contributed hardware, software, manpower, or financial support to the survey, and thus have pre-public access to data.petroMagThe Petrosian magnitude. See Magnitude, PetrosianPhotometric Pipeline (
A series of linked pipelines (Serial Stamp Collecting pipeline, SSC; Postage Stamp Pipeline, PSP, and
Frames) which analyze the raw image data, including bias
subtraction, sky and PSF determination, flat-fielding, and finding
and measuring the properties of objects. The astrometric and
photometric calibration is carried out with the astrometric
pipeline, and nfCalib.
|